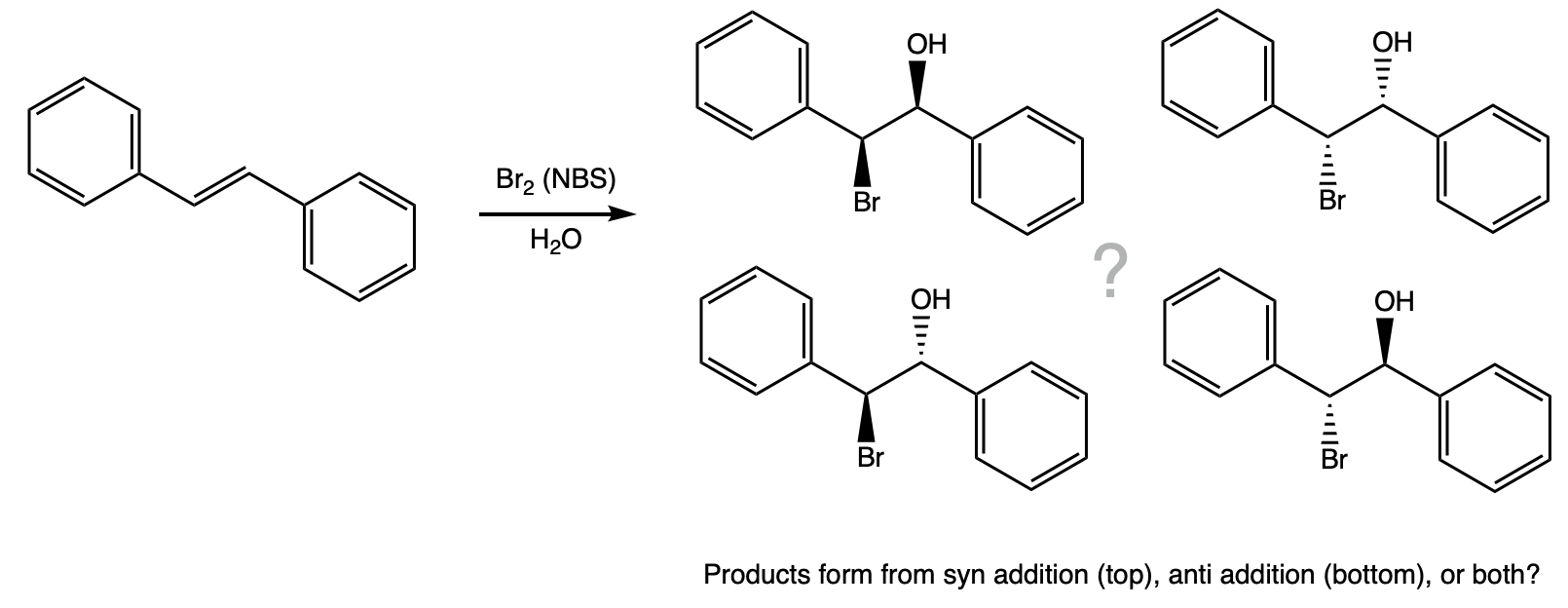

During this activity students investigate the stereochemistry of an electrophilic addition reaction. Students will carry out the reaction, purify the product by recrystallization, and identify the product based on it's melting point.
|
|
Carefully dispense 0.25 g trans-stillbene onto a piece of weighing paper. |
|
|
Add a stir bar, the trans-stillbene, 0.12 mL water, and 7 mL dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). 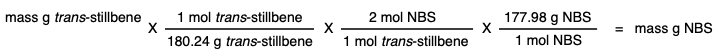
|
|
Add 2 molar equivalents of N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) in equal portions over 5 minutes. |
|
|
Pour the bright orange reaction mixture into 20 mL of ice-cold water. |
|
|
Place a piece of filter paper in the Buchner funnel, wet it with a small amount of water, and cover the filter paper with a shallow layer (~ 0.5 cm) of Celite. |
|
|
Place a piece of filter paper in the Buchner funnel, wet is with a small amount of water, and cover the filter paper with a shallow layer (~ 0.5 cm) of Celite. TIP: Press down on the funnel to make certain that a good seal has formed between the funnel and the filtering flask. TIP 2: Keep the vacuum on a low setting. A strong vacuum will cause the ether to evaporate. TIP 3: Pour slowly and slowly move the beaker while pouring. Check: Before moving to the separatory funnel step, make certain that you have two layers. |
|
Using a separatory funnel, separate the organic and aqueous layers. Return the aqueous layer to the separatory funnel and extract the aqueous layer with an additional 7 mL of diethyl ether. Combine the organic layers. |
|
Return the ether layer to the separatory funnel. Wash the ether layer with 10 mL of water; that is, add 10 mL of water to the ether layer, shake vent a few times, and pour of the aqueous layer. Wash the ether layer with 10 mL of a saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution (the satruated solution will draw some water out of the ether layer). |
|
Add a couple of scoops of anhydrous magnesium sulfate to the ether solution. After waiting a few minutes, if the magnesium sulfate still rolls around freely, continue with the activity. If the ether appears cloudy or none of the magnesium sulfate rolls around freely, add another scoop. TIP: UCLA's Prof. Bacher has a very good webpage on drying agents. |
|
Assemble a simple distillation apparatus and trransfer the ether solution to the still. Turn on the condenser water and lover the apparatus into the hot water bath. Evaporate the ether until approximately 3 mL of solution remains and transfer the 3 mL of solution to a conical vial. Evaporate the remaining 3 mL of ether using a hot water bath and a gentle stream of compressed air. TIP: To save time heating the water bath start with hot water from the tap. |
|
Warm some high-boiling petroleum ether (pet. ether) to near boiling.
Add a small amount of the hot pet. ether to the crude product, swirl the solution warm for a few minutes. Slowly add small amounts of the pet. ether to the crude product until it dissolves. TIP: Avoid adding more pet. ether than absolutely necessary. Using to much pet. ether will lower the yield of the product. |
MassDetermine the mass of the recrystallized product. |
|
Melting PointDetermine the melting point of the recrystallized product. |
