
Covalent bonds
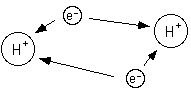
Since electrons are negative they are attracted to the nucleus because it is positive.

If two atoms get close enough together then the electrons of each atom will be attracted to both nuclii. If the atoms get two close then the nuclii will repell each other.
 |
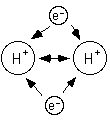 |
Single sided arrows represent attraction.
Double sided arrows represent repulsion.
Because the electrons are attracted to both nuclii pulling the two atoms apart would require energy. So, the energy of two hydrogen atoms is lower when the two atoms are together than when the two atoms are apart; that is why they stay together.
The same thing can be said for methane, CH4.
|
A C atom will attract electrons until four H's have taken position around the C atom. If a fifth H atom comes by, its electrons will not experience an attraction to the C nuclii. Why not? Lets stop and count electrons around the carbon and think about where they are. With four H's present there are ten electrons aroung the C atom. Where are these ten electrons going to go? The first two electrons fit into the n=1 shell. The next eight electrons fit into the n=2 shell. Adding the fifth H to the molecule would increase the count of electrons around the C atom to eleven. Where would the eleventh electron go? The eleventh electron would have to go into the next principal quantum level, n=3. The n=2 shell is full; the n=2 shell can hold 8 electrons, 2 in the s orbital and 6 in the p orbitals. (This is not really where the electrons go but it will demonstrate the point we want to make.) |
|
A C nucleus simply does not have enough positive charge to effectively attract that eleventh electron, because (1) the electron is farther away, and (2) there are ten electrons shielding the eleventh electron from the nucleus; that is, the eleventh electron is not attracted because the cloud of negative charge between it and the positively charged nucleus. (This is the basis for the octet rule, a rule which is violated very often by-the-way.)
So, molecules are collections of atoms which are held together by the attraction of one nucleus to the electrons of another atom. This is not a convienient way to think of molecules; so,
A bond is a pair of electrons which are shared by two nuclei.