Alkyl halides and substitution reactions
- Identify the nucleophile,
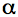 -carbon, and the leaving group in biological nucleophilic substitution reactions
-carbon, and the leaving group in biological nucleophilic substitution reactions
- Predict the products of biological nucleophilic substitution reactions based on the identified nucleophile and leaving group
- Identify the nucleophile,
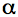 -carbon, and the leaving group in nucleophilic substitution reactions
-carbon, and the leaving group in nucleophilic substitution reactions
- Predict the products of substitution reactions
- Draw a mechanism for an SN2 reaction
- Draw a mechanism for an SN1 reaction
- Explain how the proposed mechanisms are consistent with the experimental rate law
Factors affecting substitution reactions
- Predict and understand the basis for predicting the relative abilities for substituents to serve as leaving groups
- Describe/explain the effect that the quality of the leaving group has on the rate of a nucleophilic substitution reaction
- Describe/explain the effect that the degree of substitution has on the rate of an SN1 reaction
- Describe/explain the effect that the degree of substitution has on the rate of an SN2 reaction
Factors affecting SN1 reactions
- Predict and understand the basis for predicting the relative nucleophilicities for a variety of nucleophiles
- Predict the products of reactions that involve carbocation rearrangements
- Explain how SN2 and SN1 mechanisms are consistent with kinetic data related to (1.) the degree of substitution at the C alpha to the leaving group, (2.) the quality of the leaving group, (3.) the nucleophilicity of the nucleophile, and (4.) the order of the reaction with respect to each reagent
Substitution Reactions and Stereochemistry
- Predict the stereochemical outcome of nucleophilic substitution reactions
- Explain the basis for the inversion of the stereochemstry of chiral center in an SN2 reaction
- Explain the basis for the racemization of a chiral center in an SN1 reaction
- Explain the basis for the observation of limited stereoselectivity during an SN1 reaction
- Explain how proposed SN2 and SN1 mechanisms are consitent with the stereochemical outcomes of the nucelophilic substitution reactions
- Recognize substrates that can react by both SN2 and SN1 mechanisms
Chap 8.8-9: The Competition between SN2 and SN1 mechanisms
- Explain the factors that affect the competition between SN2 and SN1 mechanisms (the role of the solvent, the degree of substitution at the alpha carbon, the role of the nucleophile)
- Determine the mechanism through which a substitution will occur based on the reaction conditions
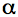 -carbon, and the leaving group in biological nucleophilic substitution reactions
-carbon, and the leaving group in biological nucleophilic substitution reactions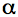 -carbon, and the leaving group in nucleophilic substitution reactions
-carbon, and the leaving group in nucleophilic substitution reactions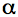 -carbon, and the leaving group in biological nucleophilic substitution reactions
-carbon, and the leaving group in biological nucleophilic substitution reactions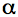 -carbon, and the leaving group in nucleophilic substitution reactions
-carbon, and the leaving group in nucleophilic substitution reactions