Chap 10: Coordination Chemistry Bonding
Goals: 10
Crystal Field Theory: 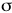 donors
donors
- Determine the hybridization of an atom based on a Kekulé structure of a molecule
- Describe the limitations of the hybridization model especially as the limitation relates to transition metals
- Describe the interactions that lead to
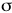 the splitting of the d orbital energy levels
the splitting of the d orbital energy levels
- Describe the primary limitation of crystal field theory
-
Goals: 10
Ligand Field Theory: 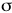 donors
donors
- Describe the interactions that lead to
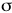 bonding between metals and ligands
bonding between metals and ligands
- Describe the effect the interactions have on the primarily metal-based molecular orbitals
- Describe the effect the interactions have on the primarily ligand-based molecular orbitals
- Use a character table to determine the irreducible representations of group orbitals for ligands that are
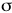 -donors
-donors
- Complete an (fill in an empty) MO diagram that involves a metal interaction with a
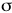 -donor
-donor
- Interpret an MO diagram that involves a metal interaction with a
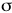 -donor
-donor
Goals: 10-10.3.2 (cont), 10.4.4
Ligand Field Theory: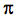 -acceptors
-acceptors
- Describe the interactions that lead to
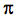 back-bonding between metals and ligands
back-bonding between metals and ligands
- Describe the effect the interactions have on the primarily metal-based molecular orbitals
- Describe the effect the interactions have on the primarily ligand-based molecular orbitals
- Complete an (fill in an empty) MO diagram that involves a metal interaction with a
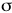 -donor,
-donor, 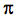 -acceptor ligand
-acceptor ligand
- Interpret an MO diagram that involves a metal interaction with a
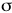 -donor,
-donor, 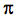 -acceptor ligand
-acceptor ligand
Ligand Field Theory: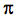 -donors
-donors
- Describe the interactions that lead to
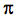 ligand-to-metal bonding between metals and ligands
ligand-to-metal bonding between metals and ligands
- Describe the effect the interactions have on the primarily metal-based molecular orbitals
- Describe the effect the interactions have on the primarily ligand-based molecular orbitals
- Complete an (fill in an empty) MO diagram that involves a metal interaction with a
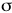 -donor,
-donor, 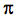 -donor ligand
-donor ligand
- Interpret an MO diagram that involves a metal interaction with a
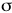 -donor,
-donor, 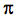 -donor ligand
-donor ligand
High- and low-spin metals
- Apply the appropriate label to a d orbital energy level diagram or generate the appropriate energy level diagram from a given label
- Describe the role that
 O, electron repulsion, and exchange energy play in determining whether a metal is high or low spin
O, electron repulsion, and exchange energy play in determining whether a metal is high or low spin
- Describe the effect that
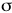 -donor,
-donor, 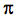 -acceptor, and
-acceptor, and 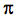 -donor ligands have on
-donor ligands have on  O
O
- Identify
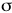 -donor,
-donor, 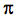 -acceptor, and
-acceptor, and 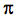 -donor ligands ligands and explain why they would be characterized as high or low field ligands
-donor ligands ligands and explain why they would be characterized as high or low field ligands
- Identify
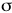 -donor,
-donor, 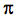 -acceptor, and
-acceptor, and 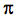 -donor ligands ligands and predict whether they are high or low field ligands
-donor ligands ligands and predict whether they are high or low field ligands
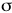 donors
donors
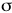 the splitting of the d orbital energy levels
the splitting of the d orbital energy levels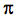 -acceptors
-acceptors
 O, electron repulsion, and exchange energy play in determining whether a metal is high or low spin
O, electron repulsion, and exchange energy play in determining whether a metal is high or low spin